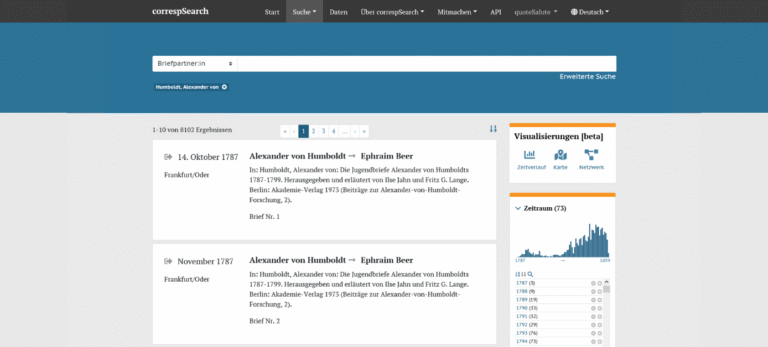
Der Webservice correspSearch wurde entwickelt um ein lange bestehendes Desiderat von Briefeditionen zu beheben: Die edierten Briefe editionsübergreifend durchsuchen zu
Short description of the project
The long-term project funded by the NRW Academy of Sciences and Arts and the Union of German Academies at the University of Bonn explores the script and language of the Classic Maya culture. It aims to document Maya hieroglyphic inscriptions in a database and to catalog the hieroglyphic language in a digital dictionary. Sources such as literature, archives, and photo collections are researched, processed in the virtual research environment TextGrid, and published online. Information and images of inscriptions are stored in an object database and in the "Maya Image Archive," an open-access repository containing over 15,000 images, freely accessible to users.
Project content
The project "Text Database and Dictionary of Classical Maya" is dedicated to the study of Maya script and language. At its core is a machine-readable corpus based on XML/TEI, designed specifically for computer-assisted research and capable of continual updates and expansions. This flexible structure facilitates the incorporation of the latest research findings and the ongoing adaptation to current developments in script studies. The corpus includes a comprehensive inventory of all relevant script and language data, including undeciphered passages that are accurately represented in hieroglyphic form and annotated both temporally and spatially. Additionally, epigraphic and linguistic analyses are conducted, and cultural-historical commentaries as well as references to secondary literature are integrated. The digital capture of these texts enables detailed linguistic evaluations, such as concordance and collocation analyses, which aid in identifying text patterns.
A significant aspect of the project is the creation of a digital grapheme inventory of Maya script within TextGrid, currently comprising about 1,000 characters and nearly 1,500 character variants, of which just over half are securely deciphered through linguistic analyses. Due to the complex nature of Maya hieroglyphs and unlike similar projects in Egyptology or cuneiform studies, it is not feasible to capture the hieroglyph texts in phonemic transliterated values. Instead, a numerical transliteration of the texts is performed using character numbers based on the digital character catalog.
To convert these numerically encoded texts into readable documents, a linguistic annotation tool was developed. This tool, created in collaboration with Dr. Cristina Vertan and named ALMAH ("Annotator for the Linguistic Analysis of Maya Hieroglyphs"), utilizes the transliteration values stored in the character catalog to create a semi-automatic phonemic transliteration of the texts. These transliterations are then manually refined and form the basis for the comprehensive Dictionary of Classical Maya, thus contributing to the scientific and cultural elucidation of this ancient language.
Add your DH research project to the project showcase by submitting a short project description via the web form. Enter project data, a brief description, a graphic or visualization as well as a detailed description of the project content with technical assignment, addressees, added value, project managers, funding information and duration.

Der Webservice correspSearch wurde entwickelt um ein lange bestehendes Desiderat von Briefeditionen zu beheben: Die edierten Briefe editionsübergreifend durchsuchen zu

is in die 1990er Jahre war es in der Filmwissenschaft ein Gemeinplatz, dass Frauen in den Anfangsjahren der Filmproduktion nur

Das Akademienvorhaben hat die philologische Erschließung und kritische Edition antiker und byzantinischer Kommentare, Paraphrasen, Kompendien und Scholien zu den Schriften

Von 1958 bis 1973 lebte und arbeitete der anglo-amerikanische Dichter Wystan Hugh Auden (1907-1973) viele Monate im Jahr im niederösterreichischen

DARIAH-DE (gefördert 2011-2019) unterstützt die mit digitalen Ressourcen und Methoden arbeitenden Geistes- und Kulturwissenschaftler/innen in Forschung und Lehre. Dazu baut

Die Virtuelle Forschungsumgebung TextGrid ist optimiert für die digitale Erschließung geisteswissenschaftlicher Quellen und deren langfristige Archivierung in einem Web-Archiv, insbesondere

DisKo steht für Diversitäts-Korpus und ist ein literaturwissenschaftliches Projekt mit Digital-Humanities-Komponente. Mit Methoden des maschinellen Lernens wollen wir einen Algorithmus

Arthur Schnitzler gehört zu den bedeutendsten österreichischen Autoren und war ein produktiver und gut vernetzter Briefschreiber. Seine Korrespondenz wurde jedoch
Wir verwenden Cookies und ähnliche Funktionen zur Verarbeitung von Daten. Die Zustimmung ist freiwillig und kann jederzeit widerrufen werden.